|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
1853 (MDCCCLIII) was
a common year starting
on Saturday of the Gregorian calendar and
a common
year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar, the 1853rd year of
the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the
853rd year of the 2nd millennium,
the 53rd year of the 19th century,
and the 4th year of the 1850s decade. As of
the start of 1853, the Gregorian calendar was 12 days ahead of the Julian
calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923. Contents · 1Events · 2Births · 3Deaths Events[edit] January–March[edit] ·
January 6 – Florida Governor Thomas
Brown signs legislation that provides public support for the
new East Florida Seminary, leading to the establishment of the University of
Florida. ·
January 8 – Taiping Rebellion: Zeng Guofan is ordered to assist the
governor of Hunan, in organising a militia force to
search for local bandits. ·
January 12 – Taiping Rebellion:
The Taiping army occupies Wuchang. ·
January 19 – Giuseppe Verdi's opera Il Trovatore premieres, in
performance at Teatro Apollo in
Rome. ·
February 10 – Taiping Rebellion:
Taiping forces assemble at Hanyang, Hankou and Wuchang, for the march on Nanjing. ·
February 12 – Puerto Montt is founded in the Reloncaví Sound, Chile. ·
February 22 – Washington
University in St. Louis is founded as Eliot Seminary. ·
March – The clothing company Levi Strauss &
Co. is founded in the United States.[1] ·
March 4 – Inauguration
of Franklin Pierce as 14th President of the United States
(his only child was killed in a train accident on January 6). ·
March 20 – Taiping Rebellion:
A rebel army of around 750,000 seizes Nanjing, killing 30,000 Imperial
troops. ·
March 29 – Manchester is granted city
status in the United Kingdom.[2][3] April–June[edit] ·
April 16 – Indian Railways: The first passenger railway
in India opens from Bombay to Thana, Maharashtra,
22 miles (35 km). ·
May ·
The
world's first public aquarium opens,
at the London Zoo. ·
An
outbreak of yellow fever kills
7,790 in New Orleans.[4] ·
Isambard Kingdom
Brunel accepts John Scott Russell's
tender for construction of the SS Great Eastern passenger
steamer. ·
May 12–October 31 – The Great
Industrial Exhibition is held in Dublin, Ireland. ·
May 23 – The first plat for Seattle, Washington is laid out. ·
June 27 – Taiping Rebellion:
The Northern Expeditionary Force crosses the Yellow River. ·
June 30 – Georges-Eugène
Haussmann is selected as préfect of the Seine (department),
to begin the re-planning of Paris. July–September[edit] ·
July 8 – U.S. Commodore Matthew C. Perry arrives in Edo Bay,
Japan, with a request for a trade treaty. ·
July 25 – Outlaw and bandit Joaquin Murrieta is killed in California. ·
July 27 – Iesada succeeds his father Ieyoshi, as Japanese shōgun. The Late Tokugawa
shogunate (the last part of the Edo period in Japan) begins. ·
August 12 – New Zealand acquires
self-government. ·
August 23 – The first true International
Meteorological Organization is established in Brussels,
Belgium. ·
The Royal
Norwegian Navy Museum is founded at Karljohansvern in Horten, perhaps the world's first naval
museum. ·
Potato chips are first prepared,
by George Crum at Saratoga
Springs, New York, according to popular accounts. ·
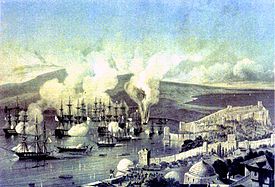
September 19 – Hudson Taylor first leaves for China. October–December[edit] Battle of Sinop, the last major naval battle
involving sailing warships. ·
October 1 – C. Bechstein's piano factory is founded, one
of three established in a "Golden year" in the history of the piano (Julius Blüthner and Steinway & Sons being the others). ·
October 4–5 – Crimean War: The Ottoman Empire begins war with Russia. ·
October 4 – On the east coast of the
United States, Donald McKay launches
the Great Republic,
the world's biggest sailing ship,
which at 4,500 tons is too large to be successful. ·
October 28 – Crimean War: The Ottoman army crosses
the Danube into Vidin/Calafat, Wallachia. ·
October 30 – Taiping Rebellion:
The Taiping Northern Expeditionary Force comes within 3 miles (4.8 km)
of Tianjin. ·
November 3 – Troops of William
Walker capture La Paz in Baja California
Territory, and declare the (short-lived) Republic of Lower
California. ·
November 4 – Crimean War: Battle of Oltenitza –
Turkish forces defeat the Russians. ·
November 15 – Maria II of Portugal is
succeeded by her son Pedro V. ·
November 30 (November 18 O.S.)
– Crimean War: Battle of Sinop – The Russian fleet
destroys the Turkish fleet. ·
December 6 – Taiping Rebellion:
French minister de
Bourboulon arrives at the Heavenly Capital, aboard the Cassini. ·
December 30 – Gadsden Purchase: The United States buys
approximately 77,000 square kilometres (30,000 sq mi) of land from
Mexico, to facilitate railroad building in the Southwest. Date unknown[edit] ·
The
Independent Santa Cruz Maya of Eastern Yucatán are
recognized as an independent nation, by the British Empire. ·
Arthur de Gobineau begins
publication of his An Essay on the Inequality of the Human Races (Essai
sur l'inégalité des races humaines). ·
Charles Pravaz and Alexander Wood independently
invent a practical hypodermic syringe. ·
Wheaton Academy is founded in West Chicago,
Illinois. ·
The Chartered
Bank of India, Australia and China is incorporated in London
by Scotsman James Wilson,
under a Royal Charter from Queen Victoria.[5][6] ·
The
Swiss watch company Tissot is founded. ·
Melbourne
Cricket Ground, a well-known sport venue in Australia, officially opens. ·
1853–1873 –
More than 130,000 Chinese laborers come to Cuba. Births[edit] January–June[edit] ·
January 1 – Karl von Einem, German general (d. 1934) ·
January 2 – Packy Dillon, American professional baseball
player (d. 1902) ·
January 10 – John Martin
Schaeberle, German-American astronomer (d. 1924) ·
Johnston
Forbes-Robertson, English actor (d. 1937) ·
Ian
Standish Monteith Hamilton, British general (d. 1947) ·
January 22 – Méry von Bruiningk,
Estonian democrat (b. 1818) ·
José Martí, Cuban revolutionary (d. 1895) ·
Vladimir
Solovyov (philosopher), Russian philosopher (d. 1900) ·
January 29 – Kitasato
Shibasaburō, Japanese physician, bacteriologist (d. 1931) ·
February 3 – Hudson Maxim, American inventor, chemist
(d. 1927) ·
February 4 – Kaneko Kentarō,
Japanese politician, diplomat (d. 1942) ·
February 6 – Ignacij
Klemenčič, Slovenian physicist (d. 1901) ·
February 18 – Ernest Fenollosa, Catalan-American
philosopher (d. 1908) ·
February 22 – Annie Le Porte Diggs,
Canadian-born state librarian of Kansas (d. 1916) ·
March 2 – Ella Loraine Dorsey,
American author, journalist, and translator (d. 1935) ·
March 5 – Howard Pyle, American artist, fiction writer
(d. 1911) ·
March 10 – Thomas Mackenzie, 18th Prime Minister of New
Zealand (d. 1930) ·
March 13 – Robert Felkin, British writer (d. 1926) ·
March 14 ·
Ferdinand Hodler, Swiss painter (d. 1918) ·
March 14 – Max Saenger, German obstetrician,
gynecologist (d. 1903) ·
March 25 – Mozaffar
ad-Din Shah Qajar, 5th Qajarid Shah of Persia (d. 1907) ·
March 29 – Elihu Thomson, English-American engineer,
inventor, co-founder of General Electric (d. 1937) ·
March 30 – Vincent van Gogh, Dutch painter (d. 1890) ·
April 1 – Marcello Amero
D'Aste, Italian admiral, politician (d. 1931) ·
April 6 – Emil Jellinek, German automobile
entrepreneur (d. 1918) ·
April 7 ·
Ella Eaton Kellogg,
American pioneer in dietetics (d. 1920) ·
Prince
Leopold, Duke of Albany (d. 1884) ·
April 8 – Laura Alberta Linton,
American chemist (d. 1915) ·
April 24 – Alphonse Bertillon,
French police officer, forensic scientist (d. 1914) ·
May 4 – Marie Robinson
Wright, American travel writer (d. 1914) ·
May 8 – Katharine Lente
Stevenson, American reformer, missionary, and editor (d. 1919) ·
May 20 – Ella Hoag
Brockway Avann, American educator (d. 1899) ·
May 28 – Carl Larsson, Swedish painter (d. 1919) ·
June 3 – William Flinders
Petrie, English Egyptologist (d. 1942) ·
June 12 – Chester Adgate
Congdon, Minnesota mining magnate (d. 1916) July–December[edit] ·
July 4 – Ernst Otto Beckmann,
German chemist (d. 1923) ·
July 5 – Cecil Rhodes, English businessman (d. 1902) ·
July 18 – Hendrik Lorentz, Dutch physicist, Nobel Prize laureate
(d. 1928) ·
July 24 – William Gillette, American actor, playwright
and stage-manager (d. 1937) ·
August 19 – Aleksei Brusilov, Russian general (d. 1926) ·
Vladimir Shukhov, Russian engineer,
polymath, scientist and architect (d. 1939) ·
Franz I,
Prince of Liechtenstein (d. 1938) ·
September 2 – Wilhelm Ostwald, German chemist, Nobel Prize laureate
(d. 1932) ·
September 6 – Katherine
Eleanor Conway, American journalist, editor, poet, and Laetare Medalist (d. 1927) ·
September 10 – Gertrud Adelborg, Swedish women's rights
activist (d. 1942) ·
September 16 – Albrecht Kossel, German physician, recipient
of the Nobel
Prize in Physiology or Medicine (d. 1927) ·
September 17 – Henry Churchill
de Mille, American dramatist, playwright; father of film
director Cecil B. DeMille (d. 1893) ·
September 20 – Chulalongkorn, Rama V, King of Siam
(d. 1910) ·
Heike Kamerlingh
Onnes, Dutch physicist, Nobel Prize laureate
(d. 1926) ·
Edmund Leighton, English painter (d. 1922) ·
September 23 – Fritz von Below, German general (d. 1918) ·
October 4 – Jane Maria Read, American poet and teacher
(unknown year of death) ·
October 13 – Lillie Langtry, English stage actress
(d. 1929) ·
October 14 – John William
Kendrick, American railroad executive (d. 1924) ·
October 17 – Grand
Duchess Maria Alexandrovna of Russia, wife of Prince Alfred, Duke
of Edinburgh (d. 1920) ·
October 26 – Tokugawa Akitake, Japanese daimyō, the last lord of Mito Domain, younger brother of the
last shōgun Tokugawa Yoshinobu (d. 1910) ·
October 30 – Louise Abbéma French painter, sculptor,
and designer of the Belle Époque (d. 1927) ·
November 9 – Stanford White, American architect (d. 1906) ·
November 13 – John Drew, Jr., American stage actor
(d. 1927) ·
November 20 – Oskar Potiorek, Austro-Hungarian general
(d. 1933) ·
December 6 – Haraprasad Shastri,
Indian academic, Sanskrit scholar, archivist and historian of Bengali
literature (d. 1931) ·
December 14 – Errico Malatesta, Italian anarchist
(d. 1932) ·
December 17 – Émile Roux, French physician, bacteriologist
and immunologist (d. 1933) ·
December 22 – Teresa Carreño,
Venezuelan pianist, singer, composer, and conductor (d. 1917) ·
December 23 – William Henry Moody,
35th United
States Secretary of the Navy, 45th United
States Attorney General, and Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United
States (d. 1917) ·
December 31 – Tasker H. Bliss, American general (d. 1930) Date unknown[edit] ·
Panagiotis Danglis,
Greek general, politician (d. 1924) ·
William
O'Malley, Irish Parliament member (d. 1939) Deaths[edit] January–June[edit] ·
January 8 – Mihály Bertalanits, Slovene (Prekmurje Slovene)
poet in the Kingdom of Hungary (b. 1788) ·
Robert Lucas,
governor of Ohio, United States (b. 1781) ·
Matteo Carcassi, Italian composer (b. 1792) ·
Archduke
Rainer Joseph of Austria, Archduke of Austria, Prince Royal of
Hungary and Bohemia (b. 1783) ·
January 19 – Karl Faber, German historian (b. 1773) ·
February 6 – Anastasio Bustamante,
4th President of Mexico (b. 1780) ·
February 15 – August,
Prince of Hohenlohe-Öhringen (b. 1784 ·
March 17 – Christian Doppler,
Austrian mathematician (b. 1803) ·
March 30 – Abigail Fillmore, First
Lady of the United States (b. 1798) ·
April 18 – William R. King, 13th Vice
President of the United States (b. 1786) ·
April 28 – Ludwig Tieck, German writer (b. 1773) ·
May 18 – Lionel Kieseritzky,
Baltic-German chess player (b. 1806) ·
June 2 ·
Lucas Alamán, Mexican statesman, historian
(b. 1792) ·
Henry
Trevor, 21st Baron Dacre, British peer, soldier (b. 1777) ·
June 8 – Richard
William Howard Vyse (b. 1784) July–December[edit] ·
July 27 – Tokugawa Ieyoshi, 12th shōgun of the Tokugawa shogunate of
Japan (b. 1793) ·
August 9 – Józef
Maria Hoene-Wroński, Polish philosopher (b. 1776) ·
August 19 – George Cockburn, British naval commander
(b. 1772) ·
August 21 - Maria Quitéria,
Brazilian national heroine (b. 1792) ·
August 23 – Alexander
Calder, first mayor of Beaumont, Texas (b. 1806) ·
August 29 – Charles James Napier,
British army general and colonial administrator (b. 1782) ·
September 3 – Augustin
Saint-Hilaire, French botanist, traveller (b. 1799) ·
September 6 – George Bradshaw, English timetable publisher
(b. 1800) ·
October 2 – François Arago,
French Catalan mathematician, physicist, astronomer and politician (b. 1786) ·
October 3 – George Onslow,
French composer (b. 1784) ·
October 5 – Mahlon Dickerson, American judge, politician
(b. 1770) ·
October 13 – Jan Cock Blomhoff,
Dutch director of Dejima, Japan (b. 1779) ·
October 22 – Juan Antonio
Lavalleja, Uruguayan military, political figure (b. 1784)) ·
October 27 – Maria White Lowell,
American abolitionist (b. 1821) ·
November 15 – Queen Maria II of Portugal (b. 1819) ·
December 15 – Georg Friedrich
Grotefend, German epigraphist, philologist (b. 1775) ·
December 23 – Juliette
Bussière Laforest-Courtois, Haitian journalist (b. 1789) Unknown date[edit] ·
Meta
Forkel-Liebeskind, German writer and scholar (b. 1765) ·
Qiu Ersao, Chinese rebel and military
commander (b. 1822) References[edit] 1.
^ Downey, Lynn (2008). "Levi Strauss: a short biography" (PDF). Levi Strauss & Co. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 23, 2011. Retrieved 1 January 2011. 2.
^ "No. 21426". The London Gazette.
1853-04-01. pp. 950–951. 3.
^ "The City of Manchester". The Guardian. Manchester. 1853-04-02.
Retrieved 2016-11-14. 4.
^ Pritchett, Jonathan B.; Tunali, Insan (1995).
"Strangers′ Disease: Determinants of Yellow Fever Mortality during
the New Orleans Epidemic of 1853". Explorations in Economic History. 32 (4):
517–539. doi:10.1006/exeh.1995.1022. 5.
^ "Our History". Standard Chartered.
Retrieved 2012-08-07. 6.
^ "Hong Kong banknotes". World
Paper Money Catalog and History. 2010. Retrieved 2012-08-07. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||