|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
1867 (MDCCCLXVII) was
a common year starting
on Tuesday of the Gregorian calendar and
a common
year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar, the 1867th year of
the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the
867th year of the 2nd millennium,
the 67th year of the 19th century,
and the 8th year of the 1860s decade. As of
the start of 1867, the Gregorian calendar was 12 days ahead of the Julian
calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923. Contents · 1Events · 2Births · 3Deaths Events[edit] January–March[edit] January 1: Roebling's
is the longest suspension bridge. February 17: Suez Canal in use. March 30: Alaska bought by check. ·
January 1 – The Covington–Cincinnati
Suspension Bridge opens between Cincinnati, Ohio and Covington, Kentuckyin the
United States, becoming the longest single-span bridge in the world. It will
be renamed after its designer, John A. Roebling, in 1983. ·
January 8 – African-American men are granted the
right to vote, in the District of Columbia. ·
January 11 – Benito Juárez becomes Mexican president
again. ·
January 30 – Emperor Kōmei of
Japan dies suddenly, age 36, leaving his 14-year-old son to succeed as Emperor Meiji. ·
January 31 – Maronite nationalist leader Youssef Bey Karam leaves Lebanon aboard a French ship, for Algeria. ·
February 3 – Shōgun Tokugawa Yoshinobu abdicates,
and the late Emperor Kōmei's son,
Prince Mutsuhito becomes Emperor Meiji of Japan in a brief
ceremony in Kyoto, ending the Late Tokugawa
shogunate. ·
February 7 – West Virginia
University is established in Morgantown,
West Virginia. ·
February 13 – The Covering of the Senne in Brussels begins.[1] ·
February 14 – Augusta Institute is
founded in Augusta, Georgia,
now known as Morehouse College.[2]. ·
February 15 – Johann Strauss II's waltz The Blue Danube (An der schönen blauen Donau) is
first performed, at a concert of the Vienna Men's Choral Association.
Strauss adapts it into its popular purely orchestral version, for the International
Exposition in Paris, later this year. ·
February 17 – The first ship passes
through the Suez Canal. ·
February 19 – Battle of Inlon River: The Qing Dynasty defeats the Nien rebels in Hubei, China. ·
February 22 – The Indiana Daily
Student is established at Indiana University, in
Bloomington. ·
February 28 – After almost 20 years (1848),
the United States
Congress forbids taxpayer funding of diplomatic envoys to
the Holy See (Vatican), and breaks
off relations.
Funding resumes, along with relations, in 1984. ·
March – The University of Illinois at
Urbana/Champaign is established (opened one year later). ·
March 1 – Nebraska is admitted as the 37th U.S. state. ·
March 5 – The Fenian Rising breaks out in Ireland.[3] ·
March 16 – An article by Joseph
Lister, outlining the discovery of antiseptic surgery, is first published in The Lancet. ·
March 23 – William III
of the Netherlands accepts an offer of 5,000,000 guilders from Napoleon III, for the sale of Luxembourg, leading to the Luxembourg Crisis. ·
March 29 – The British North
America Act receives royal assent, forming the Dominion of
Canada, in an event known as the Confederation.
This unites the Province of Canada (Quebec and Ontario), New Brunswick, and Nova Scotia on July 1. Ottawa becomes the capital, and John A. Macdonald becomes
the Dominion's first prime minister. ·
March 30 – Alaska is purchased for $7.2 million from Alexander II of
Russia, about 2 cent/acre ($4.19/km²), by United
States Secretary of State William H. Seward.
The news media call this Seward's Folly. April–June[edit] ·
April 1 – The Strait Settlement
of Singapore, formerly ruled from Calcutta, becomes a Crown colony, under the jurisdiction of
the Colonial Office in
London. ·
April 28 – I.C. Sorosis,
the first women's fraternity (sorority) founded upon the men's fraternity
model, with Pi Beta Phias its motto, is founded at Monmouth College in Monmouth, Illinois.
In 1888, the motto becomes the name of the organization. ·
May 1 – The first political May Day march takes place in Chicago.[4] ·
May 7 – Alfred Nobel patents dynamite in the United Kingdom.[5][6] ·
May 11 ·
Treaty of London:
The great powers of
Europe reaffirm the neutrality of Luxembourg, ending the Luxembourg Crisis.
The Duchy of Limburg is
formally re-incorporated into the Kingdom of the
Netherlands. ·
Cox and Box, by Francis Burnand and Arthur Sullivan, is first publicly
performed, at the Adelphi Theatre,
London. ·
May 24 – Robert William Keate becomes Lieutenant-governor of
the Colony of Natal. ·
May 29 ·
The Austro-Hungarian
Compromise (called Ausgleich in
German or kiegyezés in Hungarian (The
Compromise)) is born through Act 12, which establishes the Austro-Hungarian Empire; on June 8 Emperor Francis Joseph
of Austria is crowned King of Hungary. ·
Canadian
Confederation: Queen Victoria signs the British North
America Act, creating the Dominion of Canada, effective July 1.[7] ·
June 15 – The Atlantic Cable
Quartz Lode gold mine is named in Montana. ·
June 19 – A firing squad executes Emperor Maximilian of Mexico. July–September[edit] ·
July –
The Reverend Thomas Baker,
a Wesleyan
Methodist missionary (b.
in Playden, East Sussex, England) is cooked and eaten by
Navatusila tribespeople at Nabutautau, Fiji,
together with eight of his local followers, the last missionary in that
country to suffer cannibalism. ·
July 1 ·
Canadian
Confederation: The British North
America Act of 29 March comes into force, creating the
Dominion of Canada, the first independent dominion in the British Empire. ·
The
Constitution of the North German
Confederation comes into effect, creating a confederation of
states, under the leadership of Prussia and Otto von Bismarck. ·
July 9 – Queen's Park F.C.,
the oldest association football league
team in Scotland, is founded. ·
July 15 – France declares Cambodia's independence from Siam;
Cambodia becomes a protectorate of
France and England. ·
July 17 – In Boston, Massachusetts, the Harvard
School of Dental Medicine is established as the first dental
school in the United States. ·
July 18 – The
Battle of Fandane-Thiouthioune:
The Serer people defeat
the Muslim Marabouts of Senegambia. ·
August 7–September 20 – The first
Canadian election sees John A. Macdonald's Conservatives elected
to government. ·
August 15 – Benjamin Disraeli's Second Reform Act enfranchises many men
in cities for the first time, and adds 938,000 to an electorate of 1,057,000
in England and Wales.[8] ·
September 2 – Emperor Meiji of Japan marries Empress Shōken (née Masako Ichijō). The Empress consort is thereafter known
as Lady Haruko. ·
September 4 – The Sheffield
Wednesday F.C. is founded, at the Adelphi Hotel in Sheffield. ·
September 14 – The first volume
of Das Kapital (later
translated into English as Capital) is published by Karl Marx. ·
September 15 – The Dynamikos Sheta-Maat Spellbook: A book of the powerful hidden truth,
a grimoire by Ciara Sullivan, is
published to widespread displeasure. ·
September 30 – The United States takes
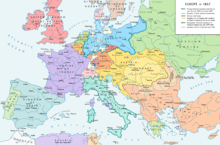
control of Midway Island. October–December[edit] Europe in 1867, after the forming of
the North German
Confederation, the Italian unification (with
the exception of the Roman part of the Papal States) and the Austro-Hungarian
Compromise. ·
October 21 – Manifest destiny – Medicine Lodge
Treaty: Near Medicine Lodge Creek, Kansas, a landmark treaty is
signed by southern Great Plains Indian
leaders. The treaty requires Native
American Plains tribes to relocate to a reservation in
western Oklahoma. ·
October 27 – Giuseppe Garibaldi's
troops march into Rome. ·
November 9 – The last shōgun of
Japan, Tokugawa Yoshinobu,
tenders his resignation to Emperor Meiji. ·
November 21 – American temperance
crusader Carrie Nation marries
Dr. Charles Gloyd. ·
November 23 – The so-called Manchester Martyrs are
hanged in Manchester, England
for the murder of a policeman, whilst attempting to rescue two members of
the Irish
Republican Brotherhood from jail. ·
December 2 – In a New York City theater, English
author Charles Dickens gives
his first public reading in the United States. ·
December 18 – Angola Horror (Buffalo, New York-area
train wreck): The fiery death of 49 people leads John D. Rockefellerto develop
and sell his Mineral Seal 300 °F Fire-Tested Burning Oil, and George Westinghouse to
invent the railway air brake,
which is mandated in the United States in 1893.[9] Date unknown[edit] ·
Pierre Michaux invents the front
wheel-driven velocipede, the first mass-produced bicycle. ·
Yellow fever kills 3,093 in New Orleans. ·
South
African diamond fields are discovered. ·
The Prohibition
National Committee is formed in the United States. ·
The Wasps Rugby Football Club is formed
in Middlesex, England. ·
At Fountain Point, Michigan, an artesian water spring begins to gush
continuously. ·
1867–1873 –
Chinese, Scandinavian and Irish immigrants lay 30,000 miles (48,000 km)
of railroad tracks in the USA. ·
Clarke School
for the Deaf in Western
Massachusetts opens its doors for the first time, becoming
the first school for the deaf in the United States to teach its children how
to communicate using the oral method. ·
The
modern rose is born, with the introduction of Rosa 'La France' by Jean-Baptiste
Guillot [fr] (1803–1882).[10][11] ·
Gorse is naturalised
in New Zealand, where
it soon becomes the worst invasive weed. ·
The Swedish
famine of 1867-1869 begin. Ongoing[edit] Births[edit] January–March[edit] ·
January 1 – Lew Fields, American vaudeville performer
(d. 1941) ·
January 5 – Dimitrios Gounaris, 94th Prime Minister of
Greece (d. 1922) ·
January 6 – Takejirō Tokonami, Japanese politician, Home
Minister, Railway Minister, and Minister of Communication (d. 1935) ·
Emily Greene Balch,
American writer, pacifist, recipient of the Nobel Peace Prize (d. 1961) ·
Thomas Coward, English ornithologist
(d. 1933) ·
January 17 – Carl Laemmle, German-born film executive
(d. 1939) ·
January 18 – Rubén Darío, Nicaraguan poet (d. 1916) ·
January 20 – Yvette Guilbert,
French singer, actress (d. 1944) ·
James
Marcus, American actor (d. 1937) ·
Ludwig Thoma,
German writer (d. 1921) ·
Maxime Weygand, French general (d. 1965) ·
January 25 – Adelaide Cabete,
Portuguese women's rights activist (d. 1935) ·
January 29 – Carl L. Boeckmann, Norwegian-American artist (d. 1923) ·
February 3 – Charles
Henry Turner, African-American entomologist (d. 1923) ·
February 4 – Alexander Godley, British general (d. 1957) ·
February 7 – Laura Elizabeth
Wilder, née Ingalls, American children's author (d. 1957) ·
February 8 – William Michael Crose, United States Navy Commander and
the seventh Naval
Governor of American Samoa (d. 1929) ·
February 10 – Charles W. Bryan, American politician
(d. 1945) ·
February 21 – Otto Hermann Kahn,
German-born American millionaire, philanthropist (d. 1934) ·
Irving Fisher, American economist (d. 1947) ·
Nina Boucicault, English actress (first ever
to play Peter Pan), daughter of Dion Boucicault (d. 1950) ·
Wilhelm
Peterson-Berger, Swedish composer (d. 1942) ·
March 4 – Charles Pelot Summerall,
American general (d. 1955) ·
March 6 – Samuel Cody, American aviation pioneer
(d. 1913) ·
March 19 – Sakichi Toyoda,
Japanese inventor, industrialist (d. 1930) ·
March 21 – Florenz Ziegfeld, Jr., American theatrical
producer (d. 1932) ·
March 25 – Arturo Toscanini, Italian conductor
(d. 1957) ·
March 26 – Arnold Theiler, founder of the Onderstepoort Veterinary
Research Institute in South Africa (d. 1936) ·
March 29 – Cy Young, American baseball player (d. 1955) April–June[edit] ·
April 2 – Eugen Sandow, German-born body builder,
circus performer (d. 1925) ·
April 7 – Holger
Pedersen, Danish linguist (d. 1953) ·
April 9 – Chris Watson, 3rd Prime
Minister of Australia (d. 1941) ·
April 10 – George William
Russell, Irish nationalist, poet and artist (d. 1935) ·
April 11 – Mark Keppel, Superintendent of Los Angeles
County Schools (d. 1928) ·
April 13 – Sammy Woods, English cricketer (d. 1931) ·
April 16 ·
René Boylesve,
French author (d. 1926) ·
Wilbur Wright, American aviation pioneer,
co-inventor of the airplane with brother Orville (d. 1912) ·
April 23 – Johannes Fibiger, Danish scientist,
recipient of the Nobel
Prize in Physiology or Medicine (d. 1928) ·
May 3 – J. T. Hearne, English cricketer (d. 1944) ·
May 7 – Władysław Reymont, Polish writer, Nobel Prize laureate
(d. 1925) ·
May 14 – Kurt Eisner, German politician, publicist
(d. 1919) ·
May 26 – Queen Mary, wife of George V of Great Britain (d. 1953) ·
June 2 – William Goodenough,
British admiral (d. 1945) ·
June 4 – Carl Gustaf
Emil Mannerheim, President of Finland (d. 1951) ·
June 6 – David T. Abercrombie,
American businessman, co-founder of Abercrombie &
Fitch (d. 1931) ·
June 8 – Frank Lloyd Wright,
American architect (d. 1959) ·
June 9 – Clarence Geldart,
Canadian-American actor (d. 1935) ·
June 14 – Joseph John Englehart, American Northwest
Frontier painter (d. 1915) ·
June 17 – Flora Finch, British-American silent film
comedian (d. 1940) ·
June 24 – J. Gordon Edwards,
American film director (d. 1925) ·
June 28 – Luigi Pirandello, Italian writer, Nobel Prize laureate
(d. 1936) ·
June 30 ·
Edward L. Beach, Sr.,
American naval officer, author (d. 1943) ·
Napoléon Turcot,
Canadian politician (d. 1939) July–September[edit] ·
July 2 – Herbert Prior, English actor (d. 1954) ·
July 8 – Käthe Kollwitz, German artist (d. 1945) ·
July 10 – Prince
Maximilian of Baden, Chancellor
of Germany (d. 1929) ·
July 25 – Alexander Rummler, American painter (d. 1959) ·
July 27 – Enrique Granados, Spanish composer (d. 1916) ·
July 28 – Charles Dillon
Perrine, American-born astronomer (d. 1951) ·
July 29 – Berthold Oppenheim,
Moravian rabbi (d. 1942) ·
July 31 – S.S. Kresge, American businessman, founder
of Kmart (d. 1966) ·
August 3 – Stanley Baldwin, Prime
Minister of the United Kingdom (d. 1947) ·
August 6 – Sam Mussabini,
English athletics coach (d. 1927) ·
August 9 ·
Charles Ballantyne,
Canadian politician (d. 1950) ·
Evelina Haverfield British suffragette (d. 1920) ·
August 11 – Hobart Bosworth, American film actor,
director, writer, and producer (d. 1943) ·
August 12 – Edith Hamilton, German-born educator, author
(d. 1963) ·
August 14 – John Galsworthy, English writer, Nobel Prize laureate
(d. 1933) ·
August 22 – Maximilian
Bircher-Benner, Swiss physician, nutritionist (d. 1939) ·
August 28 – Umberto Giordano, Italian opera composer
(d. 1948) ·
September 5 – Amy Beach, American pianist, composer
(d. 1944) ·
September 7 – Albert Bassermann, German actor (d. 1952) ·
September 16 – Vintilă Brătianu, 31st Prime Minister
of Romania (d. 1930) ·
September 21 – Charles
Bathurst, 1st Viscount Bledisloe, English politician, 4th Governor-General
of New Zealand (d. 1958) ·
September 28 – Hiranuma Kiichirō, 24th Prime Minister
of Japan (d. 1952) ·
September 29 – Walter Rathenau, German statesman, Weimar Republic foreign minister
(d. 1922) October–December[edit] ·
October 2 – James
Stevenson-Hamilton, 1st warden of South Africa's Kruger National Park (d. 1957) ·
October 12 – Lyn Harding, Welsh actor (d. 1952) ·
October 14 – Masaoka Shiki,
Japanese haiku poet (d. 1902) ·
October 16 – Mario
Ruspoli, 2nd Prince of Poggio
Suasa (d. 1963) ·
Hiranuma Kiichirō,
35th Prime Minister of
Japan (d. 1952) ·
Józef Dowbor-Muśnicki, Polish general (d. 1937) ·
October 31 – David Graham
Phillips, American journalist, novelist (d. 1911) ·
Marie Curie, Polish-born scientist, recipient
of the Nobel Prize in
Chemistry and physics (d. 1934) ·
George Paish,
English economist (d. 1957) ·
November 8 – Sadakichi Hartmann, German/Japanese critic,
poet (d. 1944) ·
November 9 – Shrimad Rajchandra, prominent Indian Jain philosopher, scholar, poet &
spiritual mentor of Mahatma Gandhi (d. 1901) ·
November 17 – Henri Gouraud, French general (d. 1946) ·
December 1 – Ignacy Mościcki, former President of Poland (d. 1946) ·
December 2 – Alec B. Francis, English actor (d. 1934) ·
December 5 – Józef Piłsudski, Polish statesman, field
marshal (d. 1935) ·
December 13 – Kristian Birkeland, Norwegian physicist (d. 1917) ·
December 14 – Ingibjörg H. Bjarnason, Icelandic politician
(d. 1941) ·
December 16 – Amy Carmichael, Irish Protestant missionary
(d. 1951) ·
December 23 – Madam C. J. Walker,
first African-American millionaire (d. 1919) ·
December 23 – Clotilde Apponyi,
Hungarian women's rights activist, diplomat (d. 1942) ·
December 26 – Yordan Milanov,
Bulgarian architect (d. 1932) Date unknown[edit] ·
Laura Anning Bell,
English artist (d. 1950) ·
Lilian Bell, American novelist and travel
writer (d. 1929) ·
Habib Pacha Es-Saad, 3rd Prime Minister and 2nd
President of Lebanon (d. 1942) ·
Florence Fuller, South African-born
Australian artist (d. 1946) ·
Zhang Haipeng,
Chinese general (d. 1949) ·
probable – Scott Joplin, American musician and composer
(d. 1917)[12] ·
Elena Meissner, Romanian women's rights
activist (d. 1940) Deaths[edit] January–June[edit] Emperor Maximilian I of
Mexico ·
January 14 – Jean-Auguste-Dominique
Ingres, French painter (b. 1780) ·
January 30 – Emperor Kōmei,
121st Emperor of Japan (b. 1831) ·
March 8 – Artemus Ward, American humorist (b. 1834)
(tuberculosis) ·
March 25 – Friedlieb Ferdinand Runge, German chemist (b. 1795) ·
April 1 – Louis du Couret,
French explorer, writer and military officer (b. 1812) ·
April 12 – David Canabarro,
Brazilian general, Gaúcho revolutionary (b. 1796) ·
April 27 – Benjamin
Hall, 1st Baron Llanover, after
whom Big Ben may be named (b. 1802) ·
May 12 – Friedrich
Wilhelm Eduard Gerhard, German archaeologist (b. 1795) ·
May 23 – William Crawshay II, Welsh industrialist (b. 1788) ·
May 29 – Margaretta Morris,
American entomologist (b. 1797) ·
June 19 – Emperor Maximilian I of
Mexico (executed) (b. 1832) July–December[edit] King Otto of Greece Metropolitan Abuna Salama III Filaret, Metropolitan of Moscow ·
July – Thomas Baker,
Methodist missionary to Fiji (b. 1832) ·
July 26 – King Otto of Greece (b. 1815) ·
July 31 ·
Benoît Fourneyron, French engineer, inventor of the
turbine (b. 1802) ·
Catharine Maria
Sedgwick, American "domestic fiction" novelist (b. 1789) ·
August 6 – David R. Porter, American politician
(b. 1788) ·
August 8 – Maria
Theresa of Austria, second Queen consort of Ferdinand
II of the Two Sicilies (b. 1816) ·
August 25 – Michael Faraday, English chemist, physicist
(b. 1791) ·
August 31 – Charles Baudelaire,
French writer (b. 1821) ·
September 10 – Simon Sechter,
Austrian music teacher (b. 1788) ·
September 26 – James
Ferguson, Scotland-born American astronomer (b. 1797) ·
October 9 – Ignacy Feliks Dobrzyński, Polish
composer (b. 1807) ·
October 11 – Gunatitanand Swami, Indian paramahamsa
of the Hindu Swaminarayan Sampraday sect (b. 1785) ·
October 23 – Franz Bopp, German linguist (b. 1791) ·
October 25 – Abuna Salama III, metropolitan of the Ethiopian Church ·
October 31 – William
Parsons, 3rd Earl of Rosse, Irish
astronomer (b. 1800) ·
November 19 – Fitz-Greene Halleck,
American poet (b. 1790) ·
November 19 – Ren Zhu, Chinese leader of the Nian Rebellion (b. 1830?) ·
December 1 – Filaret,
Metropolitan of Moscow, Russian Orthodox leader (b. 1782) ·
December 10 – Sakamoto Ryōma, Japanese samurai, politician and
businessman (b. 1836) ·
December 26 – József Kossics, Hungarian-Slovenian
Catholic priest, writer and ethnologist (b. 1788) ·
December 30 – Sarah Booth, English actress (b. 1793) References[edit] 1.
^ Demey, Thierry
(1990). Bruxelles, chronique
d’une capitale en chantier. 1.
Brussels: Paul Legrain/C.F.C.-Editions. 2.
^ College, Morehouse. "Morehouse
College - Morehouse Legacy". www.morehouse.edu. 3.
^ Moody, T. W.; Martin, F. X., eds. (1967). The
Course of Irish History. Cork: Mercier Press. p. 370. 4.
^ Haverty-Stacke, D. T.
(2009). America’s forgotten holiday: May Day and nationalism,
1867-1960. New York: New York University Press. 5.
^ "Alfred Nobel", Encyclopædia Britannica 6.
^ Schück, H.; Sohlman, R. (1929). The Life of Alfred Nobel.
London: Heinemann. p. 101. 7.
^ "Constitution Act, 1867". Department
of Justice (Canada). 2012-07-09. Retrieved 2012-08-14. 8.
^ Palmer, Alan; Veronica (1992). The Chronology of
British History. London: Century Ltd. pp. 287–288. ISBN 0-7126-5616-2. 9.
^ Charity Vogel (November 30, 2007). "The Angola
Train Wreck". American History. Retrieved October 29, 2013. 10.
^ Hessayon, D. G. The
Rose Expert. Mohn Media Mohndrunk.
p. 9. 11.
^ "La France: Hybrid Tea Rose". Archived from the original on September
22, 2009. Retrieved 2009-09-19. 12.
^ "A Biography of Scott Joplin". The
Scott Joplin International Ragtime Foundation. Archived from the
original on February 24, |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||